Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors Treatment in India
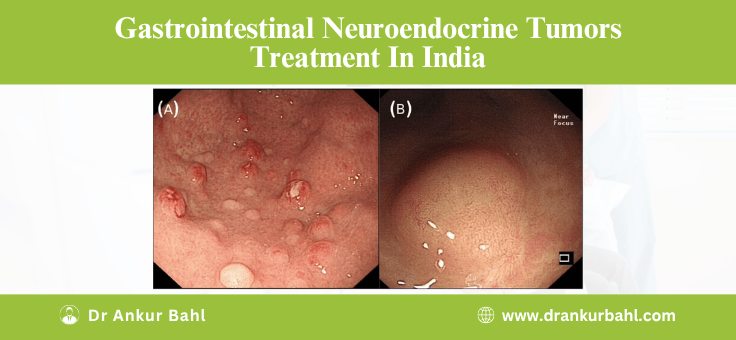
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors (GI-NETs) are rare cancers that develop in the digestive tract and require specialized, multidisciplinary treatment. India has emerged as a top destination for GI-NETs care due to its advanced medical facilities, experienced oncologists like Dr. Ankur Bahl, and significantly lower treatment costs. The complete treatment package, including diagnosis, surgery, PRRT, and post-care, typically ranges from USD 5,000 to 6,000 in India—far more affordable than in countries like the USA (USD 80,000–150,000) or Thailand (USD 25,000–40,000), making it ideal for international patients seeking expert, cost-effective care.
What Are Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors (GI-NETs)?
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumor ia a rare cancers that originate from neuroendocrine cells in the digestive system. In human body. These cells, which possess characteristics of both nerve and hormone-producing cells, are responsible for regulating digestive functions. GI-NETs can be formed in various parts of our body the GI tract including the stomach, colon, appendix, small intestine, appendix, , and rectum.
Unlike many aggressive cancers, GI-NETs tend to grow slowly, but some can behave more aggressively. Many of these tumors produce hormones, which can lead to unique symptoms and complications such as carcinoid syndrome when metastasized.
What are the Common Symptoms of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors (GI-NETs)?
There are various Symptoms that may Vary by Tumor Location.
General Symptoms (Non-functional GI-NETs)
These tumors may not secrete active hormones and often present late:
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Bloating or a feeling of fullness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation)
- GI bleeding (blood in stool or anemia)
Symptoms Based on Tumor Location
| Location | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Stomach (Gastric NETs) | Epigastric pain, indigestion, anemia, GI bleeding |
| Small Intestine (Midgut NETs) | Abdominal pain, intermittent diarrhea, bowel obstruction, flushing (carcinoid syndrome) |
| Appendix | Mimics appendicitis—RLQ pain, nausea, fever |
| Colon | Rectal bleeding, altered bowel habits, mass effect |
| Rectum | Painless rectal bleeding, rectal fullness, incidental finding on colonoscopy |
| Pancreas (pNETs) | Hormone-related syndromes (see below) or mass effect (jaundice, pain) |
| Duodenum | Ulcers, GI bleeding, obstruction |
Functional NET Symptoms (Hormone-Secreting Tumors)
| Syndrome | Hormone | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Carcinoid Syndrome | Serotonin | Flushing, diarrhea, wheezing, right heart valve disease |
| Insulinoma | Insulin | Low blood sugar, sweating, confusion, fainting |
| Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison) | Gastrin | Severe ulcers, abdominal pain, reflux |
| Glucagonoma | Glucagon | Skin rash (necrolytic migratory erythema), weight loss, diabetes |
| VIPoma | Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) | Profuse watery diarrhea, dehydration, low potassium |
| Somatostatinoma | Somatostatin | Diabetes, diarrhea, gallstones, steatorrhea |
What are the Types of GI-NETs Based on Location?
Based on location Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors (GI-NETs) categorized as:
| GI-NET Location | Common Name | Typical Behavior | Clinical Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stomach | Gastric NETs (Type I–III) | Type I & II: Indolent, Type III: Aggressive | Often asymptomatic, anemia, gastrin overproduction |
| Small Intestine (Ileum/Jejunum) | Midgut NETs | Often multiple, slow-growing, may metastasize to liver | Abdominal pain, flushing, diarrhea (carcinoid syndrome) |
| Appendix | Appendiceal NETs | Usually benign, low-grade, often found incidentally | Right lower quadrant pain, mimics appendicitis |
| Colon | Colonic NETs | Typically aggressive, poor prognosis | Bleeding, abdominal pain, change in bowel habits |
| Rectum | Rectal NETs | Often small, indolent, excellent prognosis when <1 cm | Bleeding, constipation, incidental finding on colonoscopy |
| Pancreas | Pancreatic NETs (pNETs) | Variable behavior; functional or non-functional | Hormonal syndromes (insulinoma, gastrinoma), mass effect |
| Duodenum | Duodenal NETs | Often associated with MEN-1 or gastrinomas | Ulcers, pain, GI bleeding |
| Cecum | Cecal NETs | Considered part of midgut NETs | Similar to ileal NETs—carcinoid syndrome possible |
Note:
- Midgut NETs (ileum, jejunum, cecum) are the most common GI-NETs.
- Functional NETs secrete hormones (e.g., serotonin, insulin), while non-functional NETs do not but may grow silently and metastasize.
- GI-NET behavior depends on size, grade (Ki-67 index), depth of invasion, and metastatic spread.
What are the risk factors of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors (GI-NETs)?
The risk factors of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors (GI-NETs) can be briefly described as:
- Family history of MEN1 or NF1 syndromes
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, pernicious anemia, or atrophic gastritis
- Age > 50 years
- Existing GI disorders
How GI-NETs Are Diagnosed in India?
All the top cancer centers in all over India use advanced technologies such as:
- Blood & Urine Tests: Chromogranin A, 5-HIAA, serotonin levels
- Imaging: CT scan, MRI, PET scan, MIBG scan
- Endoscopy & Capsule Endoscopy: Visualizes tumors inside the GI tract
- Biopsy: Confirms tumor type and grade
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Helps assess tumor depth
What are the Treatment Options for GI-NETs available in India?
India offers a comprehensive and cost-effective range of treatments for GI neuroendocrine tumors. Treatment is individualized based on tumor type, stage, location, and whether it has metastasized.
| Treatment Option | Purpose | Common Uses |
| Surgical Resection | Curative for localized NETs | Small bowel, appendix, stomach, pancreas, rectum |
| Endoscopic Removal | Minimally invasive option for small superficial tumors | Gastric and rectal NETs <1–2 cm |
| Somatostatin Analogs (SSA) | Hormonal symptom control & tumor stabilization | Carcinoid syndrome, midgut NETs, functional pancreatic NETs |
| Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) | Targeted internal radiation therapy | Advanced/metastatic midgut or pancreatic NETs (SSTR+ tumors) |
| Chemotherapy | Systemic treatment for aggressive or high-grade NETs | Pancreatic NETs, poorly differentiated or metastatic NETs |
| Targeted Therapy | Blocks tumor cell signaling pathways | Advanced pNETs (everolimus, sunitinib) |
| Immunotherapy (in trials) | Enhances immune response against cancer cells | High-grade or refractory NETs (research setting) |
| Liver-Directed Therapies | Controls liver metastases | NETs with hepatic metastases |
| Symptom Management & Supportive Care | Improves quality of life | Diarrhea, flushing, hypoglycemia, pain |
Why Choose Dr. Ankur Bahl for GI-NETs Treatment?
Dr. Ankur Bahl serving as Senior Director of Medical Oncology at Fortis Memorial Research Institute, is one of the leading expert in treating neuroendocrine tumors in India. With over two decades of experience, he provides personalized and evidence-based care with a multidisciplinary approach.
Highlights:
- Internationally trained oncologist
- High success rate of 99%
- Access to advanced technologies like PRRT
- Spearheading cancer research and clinical trials
- Trusted by patients worldwide for expert cancer care
What is Recovery Timeline and Follow-Up Care for Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors (GI-NETs)?
Recovery Timeline:
- Hospitalization: 3–5 days
- Return to Light Activity: 1–2 weeks
- Complete Recovery: 4–6 weeks (depends on treatment)
Follow-Up Includes:
- Routine imaging (PET/CT)
- Hormone level monitoring
- Diet & symptom management
- Surveillance for recurrence
What are the Support for International Patients Seeking GI-NETs Care in India?
India is a preferred destination for medical tourism. Patients traveling from Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and Europe receive full assistance including:
- Medical visa invitation
- Airport pickup & translation support
- Personalized treatment coordination
- Affordable accommodation & diet planning
- Post-treatment virtual consultations
GI-NET Treatment Cost Comparison: India vs. Turkey vs. USA
India is one of the most favourable destination for the affordable cancer treatment without compromising any quality.
| Treatment Type | India (USD) | Turkey (USD) | USA (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery (e.g., small bowel/pancreatic NET) | $5,000 – $8,000 | $10,000 – $15,000 | $40,000 – $70,000 |
| Endoscopic Resection (for small NETs) | $1,500 – $3,000 | $3,000 – $5,000 | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Somatostatin Analogs (monthly injection) | $500 – $1,000 | $1,000 – $1,800 | $5,000 – $8,000 |
| PRRT (Lutetium-177, per cycle) | $6,000 – $8,000 | $10,000 – $15,000 | $25,000 – $40,000 |
| Chemotherapy (Capecitabine, Temozolomide) | $700 – $1,500 | $1,500 – $3,000 | $10,000 – $25,000 |
| Targeted Therapy (Everolimus/Sunitinib) | $1,200 – $2,500 | $2,000 – $3,000 | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| PET-CT Scan | $300 – $500 | $500 – $800 | $3,000 – $6,000 |
| Ki-67, IHC, and Tumor Marker Testing | $200 – $500 | $400 – $700 | $2,000 – $4,000 |
Frequently Asked Questions
Treatment is customized based on staging, tumor location, and overall health. A full diagnostic work-up will determine if surgery is feasible.
Absolutely. Follow-up is essential to monitor for recurrence, manage hormonal symptoms, and ensure complete recovery.
GI-NETs can be curable, especially if diagnosed early and localized. In such cases, complete surgical resection of the tumor may lead to long-term remission or even cure. However, if the tumor has metastasized or is high-grade, the focus shifts to disease control and symptom management using therapies such as PRRT, hormone therapy, and targeted treatments. Many patients with GI-NETs can live for many years with appropriate, multidisciplinary care.
PRRT is a cutting-edge, targeted therapy ideal for GI-NETs that express somatostatin receptors. It uses radioactive isotopes attached to somatostatin analogs to selectively bind to cancer cells and destroy them. PRRT is especially effective in metastatic or inoperable NETs and can significantly reduce tumor burden, alleviate symptoms like flushing or diarrhea, and improve quality of life with minimal side effects.
Recovery depends on the type and extent of the surgery. After minimally invasive procedures like endoscopic resections, patients may return to light activities within a week. More extensive surgeries like bowel resections or liver surgeries may require a recovery period of 4 to 6 weeks. Indian hospitals usually recommend 3–5 days of hospitalization and follow-up plans including dietary advice, wound care, and symptom monitoring.
Yes. India has become a hub for international medical tourism. Leading hospitals offer comprehensive support services for global patients—these include medical visa assistance, airport transfers, accommodation help, language translators, personalized case coordinators, and teleconsultation post-treatment. International patients also benefit from significantly lower treatment costs, without compromising on clinical outcomes or quality.
India offers a unique combination of affordability, expertise, and advanced technology. Treatment costs in India for GI-NETs are around $5,500 to $6,000, which is a fraction of what patients would pay in the USA or Europe. India is home to internationally trained oncologists like Dr. Ankur Bahl, state-of-the-art cancer centers, and therapies like PRRT that are often not accessible or affordable elsewhere. Additionally, fast visa processes and multilingual support make it easy for international patients to receive timely, world-class care.