Penile Cancer Treatment Cost in India
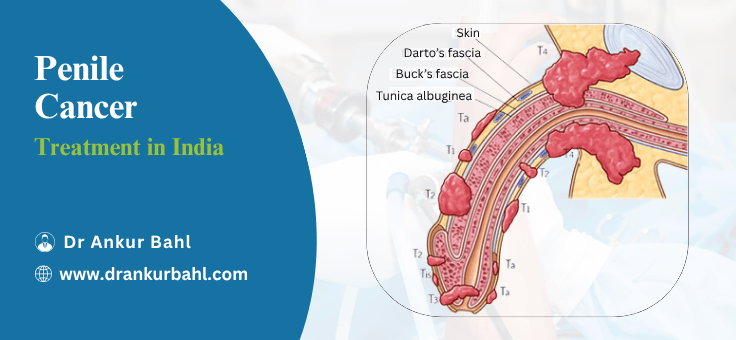
Penile cancer is a rare but serious tumor that forms on the skin or inside the tissues of the penis. It is responsible for less than 1% of male cancers worldwide, yet it can have life-altering consequences if not diagnosed and treated early. Most cases are squamous cell carcinomas, and early intervention often results in excellent long-term outcomes. Unfortunately, due to a lack of knowledge and social stigma, many patients delay treatment until the disease reaches an advanced stage.
Globally, the incidence of penile cancer varies. It is more common in parts of South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia, with reported rates of 1–2 cases per 100,000 men annually. However, access to early diagnosis and modern treatment protocols can drastically improve survival rates, even in complex cases.
When it comes to treatment affordability and medical expertise, India has emerged as a preferred destination for penile cancer care. The average cost of penile cancer treatment in India ranges from ₹3,80,000 to ₹8,50,000 (approximately $4,200 to $9,600), depending on the stage of cancer, the treatment method used (surgery, radiation, chemotherapy), and the hospital chosen. This is significantly more affordable than treatment in Western countries, where the same care could cost upwards of $25,000 to $50,000.
What Is Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer is a malignant growth that occurs on the skin or within the penis tissues. Most cases begin in the epithelial cells that line the penis, particularly in the glans (head) or foreskin. These abnormal cells can multiply uncontrollably, invade nearby tissues, and, if untreated, spread to lymph nodes or distant organs.
Penile cancer is relatively uncommon but can be aggressive, especially if the diagnosis is delayed. It most frequently affects men over the age of 50, although younger individuals with compromised immunity or certain viral infections may also be at risk.
One of the key causes linked to penile cancer is human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, particularly high-risk strains like HPV-16 and HPV-18. Other contributing factors include poor genital hygiene, phimosis (tight foreskin), chronic inflammation, smoking, and multiple sexual partners. In rare cases, prolonged use of smegma (a substance that collects under the foreskin) or exposure to ultraviolet light may also play a role.
Despite the sensitive location, penile cancer is highly treatable in early stages, primarily when localized to the surface. Treatment success often depends on how quickly the disease is identified and how well therapy is tailored to the individual's condition.
What Are the Different Types of Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer is not a single disease. It comes in several forms, each arising from a different type of cell within the penis. Identifying the specific type is critical because it guides treatment decisions and influences the overall prognosis.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): This is by far the most common type of penile cancer, accounting for nearly 95% of cases. It originates in the flat skin cells that cover the penis, especially the glans and foreskin. SCC often grows slowly and may initially appear as a sore, lump, or wart-like growth. In the early stages, it responds well to local surgery or laser treatment.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): This rare variant typically grows in the deeper layers of the skin. While less aggressive than SCC, BCC can still cause local damage if left untreated. It is usually slow-growing and seldom spreads to other organs.
- Melanoma: Penile melanoma arises from melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin. Although it is extremely rare, penile melanoma tends to be more aggressive with a higher likelihood of metastasis. Early detection is crucial, as melanoma often mimics benign skin lesions.
- Adenocarcinoma: This type develops from the glandular tissues in the penis, such as sweat glands. It is one of the rarest forms and can be hard to differentiate from other types without a biopsy. Treatment typically involves surgery and may be followed by radiation or chemotherapy.
- Sarcoma: Sarcomas form in the connective tissues, blood vessels, or muscle fibers of the penis. These are very rare but aggressive tumors that require more complex interventions. Sarcomas are often treated with wide surgical excision and may need radiation or targeted therapy.
Each type of penile cancer behaves differently, so accurate diagnosis using biopsy and pathology is key to determining the most effective treatment plan.
What Are the Symptoms of Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer often begins with subtle changes in the skin of the penis, especially on the glans (head), shaft, or foreskin. These symptoms may go unnoticed or be mistaken for minor infections, which is why early detection is sometimes delayed. Recognizing warning signs early increases the chance of successful treatment and may help avoid major surgery.
The most common symptoms to look out for are:
- Persistent Lesions or Sores: A non-healing ulcer, reddish patch, or growth that remains for more than a few weeks may indicate the onset of cancer. These lesions may bleed, become crusty, or increase in size gradually.
- Thickening or Lumps: You may notice a hardened area or mass under the skin of the penis, especially around the glans or under the foreskin. These lumps may be painless initially but can become tender or sore over time.
- Changes in Skin Color or Texture: Skin that turns bluish, darkened, or unusually shiny can be an early signal. The skin may also become rough, scaly, or develop small bumps.
- Foul-Smelling Discharge: Some men experience a bad-smelling fluid or pus from the lesion, especially if there is infection or tissue decay. It is often associated with late-stage or ulcerated tumors.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Groin: As the penile cancer progresses, it may spread to nearby lymph nodes. It leads to noticeable swelling or lumps in the groin area, which can be firm and painful.
- Pain or Discomfort: While many early-stage cases are painless, pain may occur as the tumor grows or invades deeper tissues. Discomfort during urination or sexual activity is also possible.
Any persistent or unusual change in the appearance or sensation of the penis should be examined by a specialist. Prompt diagnosis is key to avoiding complications and starting treatment at a stage when it's most effective.
What Are the Treatment Options for Penile Cancer?
Treatment for penis cancer depends on how far the disease has spread, the tumor's size and location, and the patient's overall health. Doctors usually combine surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation or immunotherapy to achieve the best outcomes.
Surgery
Surgery is the first-line treatment for most penile cancers, mainly if the tumor is localized.
- Circumcision: If the cancer is confined to the foreskin, a circumcision may be sufficient. It involves removing the foreskin and some surrounding tissue.
- Wide Local Excision (WLE): This procedure removes the penile tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue around it. It's commonly used for small, localized tumors.
- Glansectomy: When cancer affects only the head of the penis (glans), doctors may remove part or all of it. Reconstructive surgery is often done afterward to maintain function and appearance.
- Partial Penectomy: If the cancer is more extensive but hasn't spread beyond the penis, a portion of the shaft may be surgically removed. Urinary function is preserved.
- Total Penectomy: In more advanced cases, complete removal of the penis may be required. Surgeons often create a new opening in the perineum (area between the anus and scrotum) for urination. Penile reconstruction is possible later using grafts.
- Lymph Node Dissection: If the penile cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the groin, they may need to be removed through a procedure called inguinal lymphadenectomy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is used when the penile cancer has spread to lymph nodes or beyond.
- A common combination is Cisplatin and 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU), given through IV every three weeks.
- Another intense regimen is Paclitaxel, Ifosfamide, and Cisplatin (TIP), usually given in cycles lasting 3 weeks each.
- Most patients need 4 to 6 chemotherapy cycles, depending on how the body responds.
- Mild side effects like tiredness, nausea, or hair loss may occur, but medications can help manage them.
Radiation Therapy
- Radiation is often used for penile cancer when surgery is not possible or if the patient prefers a non-surgical approach.
- It is delivered externally (External Beam Radiation) over 5 to 6 weeks.
- Radiation can also be combined with low-dose chemotherapy to improve its effect.
- This method works well for small tumors and helps preserve the penis, but side effects like skin irritation or urinary discomfort may occur.
Immunotherapy
- Immunotherapy helps the immune system attack cancer cells and is considered when the disease doesn't respond to standard treatments.
- Drugs like Pembrolizumab or Nivolumab are given intravenously every 2 to 3 weeks.
- These are usually used for penile cancers that are advanced, have specific biomarkers, or are part of clinical trials.
Supportive and Palliative Care
For patients with incurable or late-stage penile cancer, supportive care focuses on comfort and symptom control. Doctors manage pain, skin wounds, and urinary issues while helping patients maintain a better quality of life.
What Is the Cost of Penile Cancer Treatment in India?
The cost of treating penile cancer in India is significantly lower than in many other developed countries, making it a preferred destination for overseas patients. On average, penile cancer treatment cost in India ranges from ₹3,80,000 to ₹8,50,000 (approximately $4,200 to $9,600), depending on the treatment type and hospital chosen.
- Circumcision or Local Excision: These minor surgeries cost between ₹60,000 to ₹1,20,000 ($720 – $1,450).
- Partial or Total Penectomy: This major surgical procedure ranges from ₹1,80,000 to ₹3,00,000 ($2,200 – $3,600).
- Lymph Node Dissection: When combined with surgery, this adds ₹80,000 to ₹1,50,000 ($950 – $1,800).
- Chemotherapy (Per Cycle): Each chemo cycle using drugs like Cisplatin or 5-FU costs between ₹40,000 to ₹70,000 ($480 – $850), with most patients needing 4–6 cycles.
- Radiation Therapy: Complete radiation treatment typically costs ₹1,50,000 to ₹2,50,000 ($1,800 – $3,000).
- Immunotherapy (if used): These advanced therapies can cost ₹2,00,000 to ₹3,50,000 ($2,400 – $4,200) per session and are generally recommended only for specific advanced cases.
How Does the Cost of Penile Cancer Treatment in India Compare with Other Countries?
India offers one of the most affordable yet high-quality options for penile cancer treatment worldwide. Here's a comparison to help you understand the savings:
|
Country |
Average Cost (USD) |
|
|
India |
$2,400 – $7,800 |
|
|
United States |
$20,000 – $50,000 |
|
|
United Kingdom |
$18,000 – $45,000 |
|
|
Turkey |
$9,000 – $15,000 |
|
|
Thailand |
$7,000 – $14,000 |
|
|
UAE |
$15,000 – $30,000 |
Why Is India So Cost-Effective?
- Lower hospital and surgeon fees
- Affordable medications (including chemotherapy drugs)
- No hidden charges for diagnostics or aftercare in most packages
- Competitive medical tourism industry
Despite the lower cost, treatment in India is provided by internationally trained oncologists, with access to robotic surgery, advanced imaging, and multidisciplinary cancer teams. Patients also benefit from shorter wait lists and personalized care plans.
What Factors Influence the Cost of Penile Cancer Treatment in India?
The final cost of penile cancer treatment in India can vary significantly based on a few essential factors. Knowing these variables can help patients plan their medical travel more effectively.
- Stage and Spread of Cancer: Early-stage penile cancer may only require minor surgery like circumcision or local excision, which is relatively low-cost. However, if the penile cancer has spread to lymph nodes or nearby tissues, the cost increases due to the need for major surgery, lymph node dissection, or chemotherapy.
- Type of Treatment Used: Different treatments come with different price tags. Minor surgeries like laser therapy or circumcision are less expensive. Partial or total penectomy and lymph node dissection require more extended hospital stays and skilled surgical care. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy add to the cost over multiple sessions. Immunotherapy, if recommended, is the most expensive due to the cost of imported drugs.
- Hospital and City of Treatment: Hospitals in metropolitan cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore may charge more due to higher infrastructure and specialist costs. However, they also offer the most advanced technology, JCI/NABH accreditation, and international patient support.
- Room Type and Hospital Stay Duration: Most Indian hospitals offer a range of room options (general ward, semi-private, private, and deluxe suites). The more luxurious the room, the higher the per-day charge. Longer ICU or post-operative stays also increase the final bill.
- Additional Services and Supportive Care: Extra services such as psychological counseling, nutrition planning, physiotherapy, pain management, or reconstructive surgery (if needed) can also impact the total cost. While not always mandatory, they can be necessary for full recovery and quality of life.
Why Choose India for Penile Cancer Treatment?
Penile cancer treatment in India combines advanced medical expertise with cost savings, without compromising on quality.
- Internationally Trained Cancer Specialists: India is home to top oncologists and urologic surgeons who are trained at renowned global institutions. Experts like Dr. Ankur Bahl are known for their extensive experience in treating complex penile cancer cases using globally accepted protocols.
- Advanced Surgical and Oncology Facilities: Leading cancer hospitals in India have the latest medical technologies, such as robotic and laparoscopic surgery, image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), and high-precision diagnostic tools like PET-CT and MRI. These tools ensure accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and faster recovery.
- Personalized Multidisciplinary Care: Indian cancer centers use a team-based approach. Surgeons, oncologists, radiologists, and support specialists work together to create a care plan tailored to each patient's condition, health status, and preferences.
- Cost Advantage with Transparent Pricing: Penile cancer treatment in India can cost up to 80% less than in countries like the US or the UK. Patients receive complete treatment packages (including surgery, chemotherapy, follow-ups, and hospital stay) at a predictable and affordable cost.
- No Waiting Period: Unlike many public healthcare systems where patients wait weeks or months for treatment, India offers immediate appointments, investigations, and surgeries, an essential factor for fast-growing cancers.
International Patient Services for Penile Cancer Treatment in India
Top hospitals in India offer a comprehensive range of services designed specifically to support international patients throughout their treatment journey. These services ensure that patients from abroad feel safe, comfortable, and well-guided every step of the way.
- Medical Visa Assistance: Hospitals provide an official medical invitation letter to help patients and their attendants secure medical visas quickly. The support team guides patients through the visa application process and documentation.
- Airport Pickup and Drop: Complimentary airport transfers are arranged to make arrivals and departures stress-free. Patients are welcomed by hospital coordinators and safely transported to their accommodation or the hospital.
- Language Support and Interpretation: Multilingual staff and professional interpreters assist patients in communicating effectively with doctors and nurses. Support is available in widely spoken languages such as Arabic, French, Spanish, Swahili, and Russian.
- Pre-Arrival and Post-Treatment Teleconsultation: Before traveling, patients can talk to the doctor online and share medical reports. After treatment, follow-up consultations are done via video or email to ensure continuity of care.
- Personalized Care Coordinator: Each international patient is assigned a dedicated coordinator who helps with booking appointments, explaining treatment plans, daily updates to family, and arranging discharge summaries and reports.
- Accommodation and Local Assistance: Hospitals assist in booking hotels or guest houses near the treatment center. Some also offer in-house international lounges or guest rooms for patients and their families.
- Help with Payments and Insurance: Assistance is available for foreign exchange payments, credit card billing, and insurance claim documentation. Support is also provided for cashless treatments with international TPAs if applicable.
What Is the Recovery Timeline After Penile Cancer Treatment?
The recovery journey after penile cancer treatment depends on the type of procedure performed, the stage of cancer, and the patient's overall health. Here's a realistic timeline and what international patients can expect after undergoing treatment in India:
Hospital Stay Duration
- For Minor Procedures (e.g., Laser Surgery or Partial Glansectomy): Hospitalization usually lasts 1 to 3 days. Most patients are discharged within 48 hours if there are no complications.
- For Major Surgeries (e.g., Partial or Total Penectomy with Lymph Node Dissection): Patients may stay in the hospital for 5 to 7 days. If reconstructive surgery is performed, the stay might be slightly more extended.
Initial Recovery Phase (First 2 Weeks)
The first two weeks are focused on wound healing and preventing infection. Patients are advised to rest, maintain hygiene, avoid strenuous activity, and follow a liquid or soft diet if general anesthesia was used.
Intermediate Recovery (3 to 6 Weeks)
Patients gradually return to daily activities, although they may still experience some discomfort or swelling. Doctors schedule follow-up visits to monitor healing and remove stitches or drainage tubes. If lymph nodes were removed, swelling in the legs may occur, and compression garments or physiotherapy may be recommended.
Return to Normal Activities (6 to 8 Weeks)
Most penile cancer patients can resume work and physical activity by 6 to 8 weeks after surgery. Sexual activity and urinary function vary depending on the surgery type. Patients undergoing partial penectomy typically adapt faster than those undergoing total penectomy.
Adjuvant Therapy Timeline (If Required)
- Chemotherapy or Radiation Therapy: These may start 3 to 4 weeks after surgery, once healing is adequate. A typical chemotherapy cycle lasts 21 days and may be repeated for 3 to 6 cycles, depending on the stage.
- Immunotherapy or Targeted Therapy: If prescribed for advanced or recurrent cases, these treatments are usually given every 2 to 3 weeks and may continue for several months.
Long-Term Monitoring
Penile cancer has a moderate recurrence risk. Regular follow-ups every 3–6 months for the first 2 years are crucial. Follow-up includes physical exams, imaging (ultrasound or CT), and sometimes biopsy of suspicious lesions.
What Is the Success Rate of Penile Cancer Treatment in India?
The success of penile cancer treatment depends on several factors, such as the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, the treatment modality used, and the expertise of the medical team. In India, patients benefit from high success rates, especially when the penile cancer is detected early and treated at top-tier cancer centers.
- Early-Stage Penile Cancer (Stage 0–I): When penile cancer is diagnosed early and confined to the surface layers of the skin, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 85–90%. Procedures like laser ablation, wide local excision, or partial glansectomy are often curative at this stage.
- Intermediate Stage (Stage II–III): If the cancer has invaded deeper tissues or spread to nearby lymph nodes, the survival rate ranges between 60–75% with appropriate surgical treatment combined with chemotherapy or radiation. Neck and groin lymph node dissection, along with adjuvant therapy, improves long-term outcomes.
- Advanced or Metastatic Stage (Stage IV): For patients with distant metastasis or locally advanced cancer, the 5-year survival drops to around 20–30%. However, palliative care, systemic chemotherapy (like TIP regimen: paclitaxel, ifosfamide, Cisplatin), and targeted therapies can prolong life and improve quality of life. Immunotherapy may offer added benefit in selected advanced cases.
Why Are Success Rates High in India?
- Use of organ-sparing techniques where possible
- Advanced diagnostics for early and accurate staging
- Access to multidisciplinary teams including urologists, oncologists, plastic surgeons, and rehabilitation experts
- Affordable care enables timely intervention without delay
- Personalized treatment planning guided by experts like Dr. Ankur Bahl ensures tailored and effective therapy
Patient Testimonials
Ahmed R., Sudan – "I Regained My Confidence After Surgery"
After being diagnosed with early-stage penile cancer, I was scared of what the future held. I flew to India for treatment under Dr. Ankur Bahl and underwent partial penectomy with excellent cosmetic results. The care team was respectful, professional, and ensured my dignity throughout. Today, I'm cancer-free and back to my normal life.
Carlos M., Peru – "The Decision to Come to India Saved My Life"
My cancer had already spread to the lymph nodes. I received chemotherapy followed by surgery at a top hospital in Gurgaon. The treatment was intense but well-managed. Within six months, my scans were clear. Thanks to India's advanced care and Dr. Bahl's team, I was given a second chance at life.
Samuel K., Kenya – "Affordable, World-Class Treatment"
I couldn't afford cancer treatment back home. A friend recommended India, and I'm glad I made the trip. My surgery was successful, and the hospital arranged everything from a visa to accommodation. The cost was a fraction of what I expected, and the quality was outstanding.
Faisal A., Saudi Arabia – "From Fear to Freedom"
I was hesitant at first, but the international patient team at the hospital made everything easy. Dr. Ankur Bahl was compassionate and explained every step of my chemotherapy and follow-up. I felt respected and cared for. I'm in remission and forever grateful.
Frequently Asked Questions
The average cost of penile cancer treatment in India ranges between ₹3,80,000 to ₹8,50,000 ($4,200 to $9,600), depending on the stage of cancer and treatment approach.
Yes, India offers penile cancer treatment at 60–80% lower cost than in countries like the USA, UK, or Australia, with no compromise on care quality.
The cost typically includes the surgeon's fee, anesthesia, hospital stay, diagnostic tests, medications, and post-operative care. However, it may exclude long-term follow-up and travel.
Yes, top hospitals in India offer surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and penile reconstruction for all stages of penile cancer.
Most patients need to stay for about 2–3 weeks for surgery and recovery. If chemotherapy is planned, multiple cycles may extend the stay to 6–8 weeks or more.
Yes, if detected early, penile cancer is highly curable with surgery or local therapies. Advanced cases can be managed with a combination of treatments.
Most private Indian hospitals accept international health insurance or work with medical tourism partners to assist with claims and billing documentation.
Absolutely. Dedicated international patient departments help with visas, accommodation, translators, airport pickups, and personalized care coordination.