Vaginal Cancer Treatment Cost in India
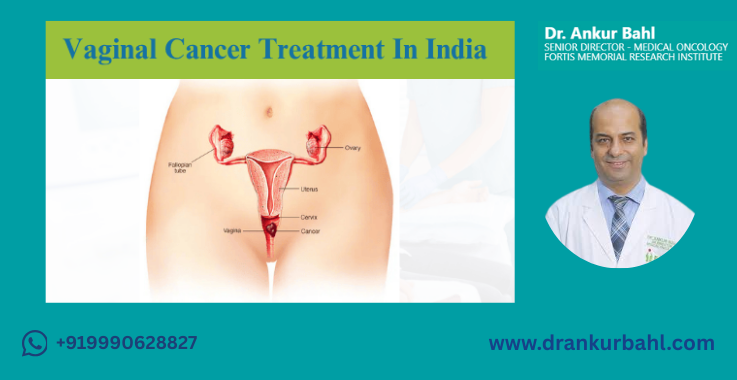
Vaginal cancer is a rare but serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and a combination of specialized treatments for the best outcome. It mainly affects the cells lining the vagina and is more common in women over 60, though it can occur at younger ages too, especially in those with an HPV infection.
The cost of vaginal cancer treatment in India typically ranges between ₹2,00,000 and ₹6,50,000 (approximately $2,400 to $7,800). The price depends on the stage of the cancer, the type of treatment required (surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy), hospital facilities, and the duration of care. Despite being highly affordable compared to countries like the US, UK, or Australia, India provides international standards of treatment with top oncologists and advanced technologies.
What Is Vaginal Cancer?
Vaginal cancer is a rare malignancy that begins in the tissues of the vagina—the muscular canal that connects the uterus to the external genitalia. While it accounts for only 1% to 2% of all gynecologic cancers, it requires prompt attention and treatment due to its potential to spread to nearby organs.
How It Develops
Vaginal cancer usually starts when normal cells in the vaginal lining undergo genetic changes (mutations) that cause them to multiply uncontrollably. Over time, these abnormal cells can form a tumor and may eventually invade nearby structures, such as the cervix, bladder, or rectum.
How It Spreads
If left untreated, vaginal cancer can spread through:
- Direct extension to nearby reproductive or urinary organs
- Lymphatic spread to pelvic or inguinal lymph nodes
- Bloodstream metastasis, although rare, to organs like the lungs or liver
What Are the Types of Vaginal Cancer?
Vaginal cancer can arise from different types of cells in the vaginal tissue. Each type behaves differently and may require a unique treatment approach. Here are the major types:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: It is the most common type, making up around 80% to 90% of all vaginal cancer cases. It begins in the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the vagina. This form of cancer tends to grow slowly but can eventually spread to nearby organs if not treated promptly.
- Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma originates in the glandular cells that produce vaginal fluids. Although less common than squamous cell carcinoma, it has a higher tendency to spread to distant parts of the body. This type is more often seen in older women.
- Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma: It is a rare subtype of adenocarcinoma typically associated with women whose mothers took diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy in the 1950s to 1970s. It often affects younger women and requires close monitoring due to its aggressive nature.
- Melanoma of the Vagina: Though most people associate melanoma with the skin, it can develop in mucosal tissues like the vagina. Vaginal melanoma is very rare and tends to be aggressive. Treatment typically involves surgery and may include immunotherapy.
- Vaginal Sarcoma: Sarcomas begin in the connective tissues, muscles, or blood vessels of the vagina. It is extremely rare and is often diagnosed in younger females. It may require extensive surgery followed by radiation or chemotherapy.
What Are the Symptoms of Vaginal Cancer?
Vaginal cancer often develops slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. This is why it's frequently detected during routine gynecological exams. As the tumor progresses, certain signs and symptoms may appear.
Early-Stage Symptoms
Initially, symptoms may be vague or mistaken for minor infections. These can include:
- Women may notice unusual vaginal discharge, which is watery, bloody, or persistent without a clear cause.
- There might be light vaginal bleeding, especially after intercourse, between periods, or after menopause.
- A lump or mass in the vagina could be felt, either during hygiene routines or sexual activity.
- Some women may experience pain during sex (dyspareunia) or mild pelvic discomfort.
Advanced-Stage Symptoms
As the vaginal cancer spreads, the symptoms tend to become more specific and intense:
- Pelvic pain or pressure that becomes consistent and does not go away
- Painful or difficult urination or bowel movements
- Constipation that does not respond to usual remedies
- Swelling in the legs, especially if lymph nodes are involved
- Chronic fatigue or unintentional weight loss in advanced cases
Why Vaginal Cancer Is Often Misdiagnosed
The symptoms of vaginal cancer can mimic common conditions like vaginal infections, urinary tract infections, or menopause-related changes. It often leads to delayed diagnosis. Women are encouraged to seek medical attention if any unusual vaginal symptoms persist for more than two weeks, especially after menopause.
Treatment Options for Vaginal Cancer
The treatment approach for vaginal cancer depends on multiple factors, including the type of cancer, its size, stage, and location, as well as the patient's age and overall health. Doctors may use one or a combination of the following therapies to effectively treat the disease.
Surgery
Surgery is the first-line treatment for early-stage vaginal cancer. The type of surgical procedure depends on how far the cancer has spread.
- Local excision may be performed for tiny tumors, where only the cancerous tissue is removed.
- Vaginectomy involves the removal of part or all of the vaginal canal and is used in more advanced cases.
- Pelvic exenteration, a more extensive surgery, may be needed if the cancer has spread to surrounding organs such as the bladder or rectum.
Surgery may also include lymph node dissection to check for spread.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is commonly used in both early and advanced stages of cancer. It can be given as the primary treatment or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) targets the tumor from outside the body, typically over several weeks.
- Brachytherapy involves placing a radioactive source inside the vagina to deliver high-dose radiation directly to the tumor.
Radiation is especially effective in squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be used when the cancer has spread beyond the vagina or does not respond to other treatments. It is often combined with radiation therapy (called chemoradiation) to enhance its effect.
Common drugs include cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil, given in cycles depending on the treatment plan. Chemotherapy may also be used if the cancer returns after initial treatment.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
While still under research for vaginal cancer, targeted therapies that attack specific cancer cell markers may be used in select cases. Drugs like bevacizumab (anti-angiogenesis) are occasionally used in recurrent or metastatic cases.
Immunotherapy is another emerging option, especially for HPV-related vaginal cancers, although it is not yet a standard treatment in all hospitals.
Palliative and Maintenance Care
For advanced-stage patients, palliative care focuses on managing symptoms like pain, bleeding, or difficulty urinating. Maintenance therapies may be used to slow disease progression after initial treatment has been started.
What Is the Cost of Vaginal Cancer Treatment in India?
The cost of vaginal cancer treatment in India is significantly lower. International patients benefit from expert oncologists, modern infrastructure, and comprehensive treatment packages at a fraction of the price they would pay back home.
On average, the total cost of vaginal cancer treatment in India ranges from ₹2,00,000 to ₹6,50,000 ($2,400 to $7,800). It includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hospital stay, diagnostic tests, and supportive care.
Surgical Costs
- For early-stage vaginal cancer, local excision surgery may cost between ₹80,000 and ₹1,50,000 ($960 to $1,800).
- More extensive procedures like vaginectomy or pelvic exenteration could range between ₹1,50,000 and ₹3,00,000 ($1,800 to $3,600).
- Costs may increase with the need for reconstructive surgery or lymph node dissection.
Radiation Therapy
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) typically costs around ₹1,20,000 to ₹2,50,000 ($1,440 to $3,000) for a full course of 30–35 sessions.
- If brachytherapy is added, the cost may range from ₹1,00,000 to ₹1,80,000 ($1,200 to $2,160).
Chemotherapy
- Each chemotherapy cycle may cost ₹25,000 to ₹40,000 ($300 to $480), depending on the drugs used.
- A complete course (4–6 cycles) would cost around ₹1,00,000 to ₹2,40,000 ($1,200 to $2,900).
Targeted Therapy (if applicable)
- In rare or advanced cases, targeted drugs like Bevacizumab (Avastin) may be prescribed. The cost per dose ranges from ₹75,000 to ₹1,50,000 ($900 to $1,800).
Diagnostics and Hospital Stay
- Pre-treatment diagnostics, including imaging, biopsies, blood tests, and consultation, typically cost between ₹40,000 to ₹1,00,000 ($480 to $1,200).
- Hospital stay in a private room for 3–5 days is usually included in most surgical packages.
How Does the Cost in India Compare with Other Countries?
One of the many reasons overseas patients choose India for vaginal cancer treatment is the huge cost advantage, without compromising on medical quality, safety, or expertise. In fact, India offers world-class cancer care at just a fraction of the fees charged in Western nations.
|
Country |
Average Treatment Cost (USD) |
Notes |
|
India |
$2,400 – $7,800 |
Includes surgery, radiation, chemo, and stay |
|
USA |
$25,000 – $60,000 |
High hospital charges and doctor fees |
|
UK |
$20,000 – $45,000 |
Long waiting times for NHS patients |
|
UAE |
$18,000 – $40,000 |
Expensive private care |
|
Singapore |
$22,000 – $50,000 |
High-quality care but costly |
|
Thailand |
$10,000 – $18,000 |
Affordable but limited gynecologic oncology centers |
Why Is India More Affordable?
The major reasons why vaginal cancer treatment is more cost-effective in India include:
- Lower cost of medical infrastructure and labor compared to Western countries.
- No hidden administrative fees, and most hospitals offer bundled packages for international patients.
- Competitive medical tourism market, which ensures hospitals maintain affordable pricing to attract overseas patients.
- Government-regulated drug pricing in India makes chemotherapy and cancer medications more affordable than in countries like the US.
So, while a patient in the US may have to spend over $50,000 for comprehensive care, the same treatment in India would cost as little as $2,500 to $7,500, including hospital stay, diagnostics, and doctor consultations. It enables international patients to receive timely and high-quality care without incurring a financial burden.
What Factors Affect the Cost of Vaginal Cancer Treatment?
The overall cost of vaginal cancer treatment in India can vary widely from patient to patient. This is because several key factors influence how much a patient may need to pay. Knowing these factors helps patients and their families plan more effectively and avoid unexpected medical expenses during their treatment journey.
- Stage and Type of Cancer: The cost is usually lower for early-stage vaginal cancer, where local excision or limited radiation is sufficient. Advanced stages of vaginal cancer often require a combination of surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and extended hospital stays, which can increase the total cost significantly.
- Type of Treatment Required: Each treatment has its own specific pricing. Patients who need only radiation or surgery will pay less than those needing multiple therapies like chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or brachytherapy. The choice of treatment is based on the tumor size, spread, and the patient's condition.
- Hospital and City Chosen: Top-tier hospitals in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, and Chennai may charge more due to world-class infrastructure and advanced technologies. However, even these prices are affordable compared to international standards.
- Doctor's Expertise and Surgical Complexity: Experienced oncologists and robotic surgery options can improve outcomes, but may carry a higher cost. If complex surgeries like pelvic exenteration or vaginal reconstruction are needed, the surgical fee and OT charges can rise accordingly.
- Diagnostic and Imaging Requirements: PET scans, MRI, CT scans, biopsies, and pathology reports are necessary to assess the stage of cancer and plan treatment. These diagnostic services may add ₹40,000 to ₹1,00,000 ($480–$1,200) to the overall cost.
- Length of Hospital Stay: Basic surgical cases typically require 3 to 4 days of hospitalization. However, complicated surgeries or combined treatments may need ICU care or a longer stay, which adds to room charges and nursing care expenses.
Why Choose India for Vaginal Cancer Treatment?
India has become a trusted destination for international patients seeking affordable and high-quality cancer care. With top oncologists, advanced hospitals, and personalized attention, India offers a strong value proposition—especially for those dealing with rare and complex cancers like vaginal cancer.
- Globally Renowned Oncologists: India is home to some of the world's best cancer specialists, including highly skilled gynecologic oncologists trained in leading institutions from the US, UK, and Europe. Experts like Dr. Ankur Bahl, a senior medical oncologist at Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon, are well-known for managing complex gynecological cancers using the latest evidence-based approaches.
- World-Class Hospitals with International Accreditation: Hospitals such as Fortis are JCI- and NABH-accredited, ensuring adherence to strict quality standards, effective infection control, and optimal patient safety. These facilities offer advanced diagnostics, robotic surgery, radiation oncology units, and integrated cancer care under one roof.
- Affordable Yet Comprehensive Packages: Indian hospitals offer all-inclusive treatment packages at a fraction of global costs. These include consultations, diagnostics, surgery, radiation therapy, medications, hospital stays, and follow-up care.
- Minimal Waiting Time for Treatment: Unlike in many Western countries, where patients often face lengthy waiting periods, treatment in India can commence within days of diagnosis.
- Language, Culture, and International Services: Most Indian healthcare staff and doctors speak fluent English. Additionally, hospitals offer language interpreters, multilingual coordinators, customized diet plans, and accommodations for patients from Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and beyond, including those with religious or cultural needs.
- High Success Rates in Treating Vaginal Cancer: Thanks to early diagnosis, skilled surgical teams, and modern treatments, vaginal cancer survival rates in India are on par with global standards. Many hospitals maintain 5-year survival rates of 70% or higher for early-stage cases, with even advanced-stage patients receiving effective palliative care and symptom control.
Choosing India means selecting timely, effective, and budget-friendly cancer care, backed by a team of experts who genuinely care about their patients.
International Patient Services Offered in India
India has become a global hub for medical tourism, particularly for patients seeking cancer treatment. Hospitals across India have dedicated international patient departments designed to make your entire journey comfortable, organized, and stress-free.
- Visa Assistance and Invitation Letters: Indian hospitals provide medical invitation letters that facilitate the issuance of medical visas for patients and their accompanying family members. Many hospitals also guide you step-by-step through the visa application process to avoid delays.
- Free Airport Pickup and Drop: Once your travel is scheduled, the hospitals arrange complimentary airport pickup and drop for you and your attendants. A hospital representative meets you at the airport and ensures a smooth check-in process at the hospital or accommodation.
- Language Interpreters and Translation Services: Language is never a barrier. Hospitals in India offer professional interpreters for Arabic, French, Swahili, Russian, Bangla, and more. All medical discussions, reports, and discharge summaries can be translated into your preferred language upon request.
- Affordable Accommodation Near Hospitals: If you prefer to stay outside the hospital before or after treatment, the hospital staff can assist you in finding budget hotels, guesthouses, or serviced apartments nearby.
- Dedicated International Patient Coordinators: Each patient is assigned a personal coordinator who helps with everything—from scheduling doctor appointments to organizing tests, arranging treatment packages, and providing daily updates. These coordinators act as your single point of contact during your entire stay.
- Currency Exchange and SIM Card Support: Many hospitals offer currency exchange services at competitive rates and assist you in getting a local SIM card for easier communication.
- Religious and Dietary Customization: Hospitals understand and respect different cultures. Halal food, vegetarian meals, prayer facilities, and religious accommodations are available upon request, ensuring your comfort and well-being.
With these international patient services, India offers not just treatment but an entire healing experience that feels safe, supported, and welcoming.
What Is the Success Rate of Vaginal Cancer Treatment in India?
The success rate of vaginal cancer treatment in India has shown promising results, especially when the cancer is treated in the early stages. Indian hospitals adhere to globally recognized treatment protocols, and their outcomes are comparable to those of top centers in the US and Europe.
Survival Rates Based on Stage
- For early-stage vaginal cancer (Stage I), the 5-year survival rate in India can be as high as 75% to 85%, especially with timely surgery or radiation therapy.
- For Stage II, survival rates typically range between 55% to 70%, depending on the size and spread of the tumor.
- For advanced stages (Stage III or IV), the 5-year survival rate ranges from around 30% to 50%. However, combined treatments (chemoradiation, surgery, targeted therapy) still offer reasonable symptom control and improved quality of life.
Many women treated for vaginal cancer in India report a significant improvement in their quality of life after treatment. With proper rehabilitation and emotional support, patients often return to their regular routines, relationships, and work within a few months after completing treatment.
What Is the Recovery Timeline for Vaginal Cancer Treatment?
Recovery after vaginal cancer treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the type of treatment received, and the overall health of the patient. In most cases, vaginal cancer patients can gradually return to their routine over several weeks.
Recovery After Surgery
If surgery is part of the treatment, the initial hospital stay usually lasts 3 to 5 days. Patients who undergo extensive procedures, like a pelvic exenteration, may stay longer. After discharge:
- Most women require 2 to 4 weeks of rest at home before resuming light activities.
- Complete recovery from surgery may take 6 to 8 weeks, especially if reconstruction or lymph node dissection was performed.
- During this time, vaginal cancer patients are advised to avoid lifting heavy objects, strenuous physical activity, or sexual intercourse.
Recovery from Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation is typically given over 5 to 7 weeks, with daily sessions. Side effects such as fatigue, vaginal dryness, and skin irritation around the pelvic area may continue for a few weeks after completion.
- Patients can slowly resume normal activities but should monitor for potential late side effects, such as bowel or bladder discomfort.
- Most women report improvement within 4 to 6 weeks after finishing treatment.
Chemotherapy Recovery Timeline
Chemotherapy is administered in cycles over several months, depending on the cancer stage and regimen.
- Common adverse effects include nausea, hair loss, fatigue, and low blood counts.
- Between cycles, patients often need 1–2 weeks of rest, and complete recovery of energy may take 1–3 months after the final dose.
- Blood tests and follow-ups help monitor progress and guide further care.
Returning to Normal Life
Most patients are encouraged to gradually resume their work or daily routines within 2 to 3 months after completing treatment. Patients require regular follow-ups every 3–6 months during the first two years to monitor their progress and ensure optimal treatment outcomes. Seek counseling to cope with emotional and physical changes after treatment.
Patient Testimonials
India is a trusted destination for vaginal cancer treatment among patients from around the world, especially from Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe. Many international patients choose Indian hospitals for their combination of affordable care, advanced treatments, and compassionate medical support. Here are a few representative stories:
Ayana, 54 – Nigeria
"I was diagnosed with vaginal cancer after experiencing unexplained bleeding. In Nigeria, I was advised to go abroad, but Europe was too expensive. I found Fortis Gurgaon through a friend. Dr. Ankur Bahl and his team gave me hope. Within three weeks, I started radiation and chemotherapy. The care was world-class. I was treated like family. I've been in remission for over a year now."
Aaliyah, 49 – Oman
"My gynecologist suspected cancer and asked me to seek quick treatment. A medical facilitator connected me to Fortis Hospital in India. Dr. Ankur Bahl was very honest and reassuring. He explained every step. The hospital helped us with everything—visa, airport pickup, and an Arabic translator. I had surgery, and recovery went smoothly. I'm back home now and feel stronger than ever."
Maryam, 42 – Kenya
"I had pain and discharge for months. In Kenya, doctors were unsure. In India, within three days, I had a confirmed diagnosis. Dr. Ankur Bahl at Fortis suggested a combined chemoradiation approach. The cost was affordable, and the hospital was modern and clean. I am now cancer-free. Thank you, India, for saving my life."
Sara, 45 – Iraq
"My biggest worry was being alone in a different country. But Fortis provided an Arabic-speaking coordinator who stayed with me throughout. Dr. Ankur Bahl answered every question with kindness. The radiation and chemo sessions were painless, and they provided food that matched my cultural needs. India made me feel safe and respected."
Frequently Asked Questions
Vaginal cancer is a rare form of cancer, accounting for less than 2% of all gynecologic cancers. However, it is more likely to occur in women over the age of 50 and those with a history of HPV infection.
The most common cause is persistent infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Other risk factors include smoking, previous cervical cancer, and a history of radiation therapy to the pelvic region.
Yes. Routine pelvic exams and Pap smears can help detect early signs of vaginal cancer. However, because early-stage symptoms are often mild or absent, regular check-ups are crucial.
If detected in the early stages, vaginal cancer is highly treatable and often curable with surgery, radiation, or a combination of both. Advanced stages require more complex treatment, but remission is possible.
Treatment depends on the stage and type of the condition. Common approaches include radiation therapy, surgery (such as wide excision or pelvic exenteration), chemotherapy, or combined therapy for advanced cases.
In most cases, treatment affects fertility, especially if surgery or radiation involves the reproductive organs. Your oncologist will discuss fertility preservation options if needed.
Yes, typical side effects include fatigue, vaginal dryness or scarring, bowel or urinary changes, and emotional impact. These are often temporary and manageable with supportive care.
Vaginal cancer surgery requires a hospital stay of 3–5 days with a few weeks of recovery. Radiation typically takes 5–7 weeks, while chemotherapy is given in cycles over several months.
The cost of vaginal cancer treatment in India typically ranges from ₹2,00,000 to ₹6,00,000 ($2,400 to $7,200), depending on the stage, hospital, and type of treatment (surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination of these).
The total cost includes doctor consultations, hospital stay, surgery charges, radiation therapy sessions, chemotherapy cycles, diagnostic tests (such as biopsies and PET/CT scans), and follow-up care.
Most top hospitals in India offer transparent billing. Packages usually include all major expenses; however, additional costs may arise for an ICU stay or complications.
Yes. Treatment in India is 60–80% more affordable compared to the US, UK, or Gulf countries, without compromising on medical quality.
Absolutely. Most Indian hospitals, including Fortis Gurgaon, provide pre-arrival treatment quotes based on medical reports.